Paediatric eye care, Squint
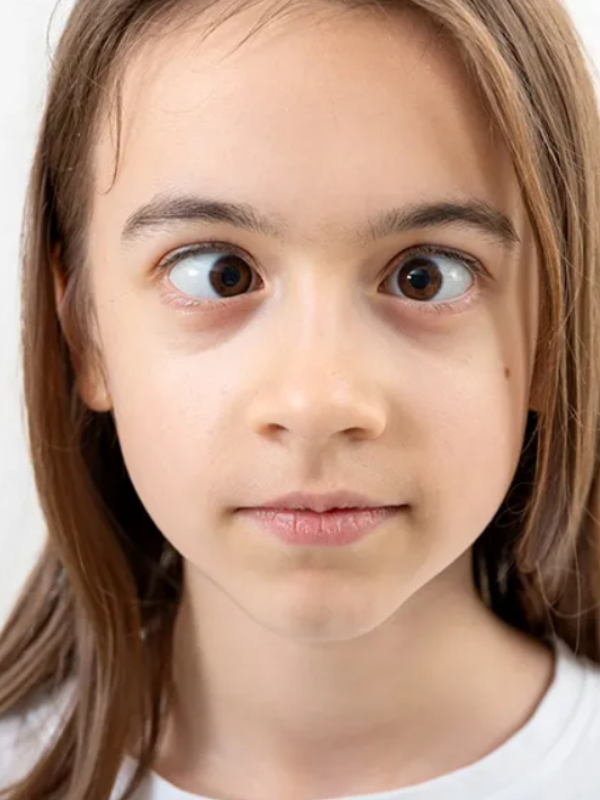

A squint, or strabismus, is a condition in which the eyes are misaligned and do not focus on the same point simultaneously. This misalignment can affect one or both eyes and lead to double vision, impaired depth perception, and difficulty with visual development.
What is Myopia?
Why is Paediatric Eye Care Important?
- Early detection prevents developmental delays: Vision issues can affect a child’s learning and development.
- Screening identifies congenital or acquired conditions: Early detection ensures timely treatment.
- Prevention of long-term complications: Some eye conditions can lead to permanent vision loss if untreated.
Regular paediatric eye exams should begin in early childhood to ensure healthy vision development.
Common Paediatric Eye Conditions
Parents, teachers, or individuals should watch for these signs in children and adults:
- Squinting to see distant objects.
- Complaints of blurry vision when viewing objects far away.
- Difficulty reading road signs or seeing the TV clearly from a distance.
- Frequent headaches, especially during or after near work.
Regular eye exams can confirm myopia even if no symptoms are evident.
Treatment of Squint (Strabismus)
The treatment for squint depends on the type of misalignment, severity, and underlying cause. Treatment strategies aim to correct alignment, improve vision, and prevent complications like amblyopia.
1. Prescription Glasses or Contact Lenses
If the squint is caused by refractive errors like myopia or hyperopia, prescription eyewear can help correct alignment by improving focus.
2. Vision Therapy or Orthoptics
- Orthoptics involves eye exercises that strengthen the eye muscles and improve coordination between the two eyes.
- Activities and exercises are tailored to the child’s condition and may involve:
- Eye exercises to strengthen weak eye muscles.
- Coordination activities to enhance eye movement.
- Improving binocular vision and depth perception.
3. Eye Patching for Amblyopia
If squint leads to amblyopia (lazy eye), treatment involves patching the stronger eye to force the weaker eye to strengthen and develop.
Prevention & Early Intervention
Paediatric eye care focuses on early detection and prevention. The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends:
- Routine eye screening for all children during their first few years of life.
- Early treatment of refractive errors and squint to avoid complications.
- Monitoring children for any visual difficulties or eye alignment problems.
Early intervention is crucial to improve visual outcomes and support a child’s learning and development.